What'S Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction ?
Overview
Adult-acquired flatfoot or collapsed arch occurs because the large tendon on the inside of the ankle - the posterior tibial tendon - becomes stretched out and no longer supports the foot?s arch. In many cases, the condition worsens and and the tendon thickens, becoming painful, especially during activities. Flatfoot or collapsed arch is also known as posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. This condition is different than having flat feet since birth (known as congenital flatfoot), although sometimes these patients develop similar symptoms and require similar treatments. 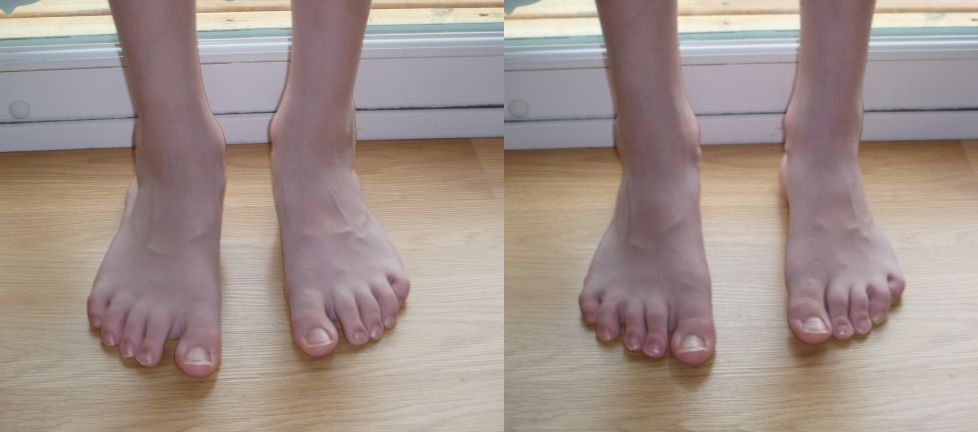
Causes
Flat feet causes greater pressure on the posterior tibial tendon than normal. As the person with flat feet ages, the muscles, tendons and ligaments weaken. Blood supplies diminish as arteries narrow. These conditions are magnified for obese patients because of their increased weight and atherosclerosis. Finally, the tendon gives out or tears. Most of the time, this is a slow process. Once the posterior tibial tendon and ligaments stretch, body weight causes the bones of the arch to move out of position. The foot rotates inward (pronation), the heel bone is tilted to the inside, and the arch appears collapsed. In some cases, the deformity progresses until the foot dislocates outward from the ankle joint.
Symptoms
Patients will usually describe their initial symptoms as "ankle pain", as the PT Tendon becomes painful around the inside of the ankle joint. The pain will become more intense as the foot flattens out, due to the continued stretching and tearing of the PT Tendon. As the arches continue to fall, and pronation increases, the heel bone (Calcaneus) tilts into a position where it pinches against the ankle bone (Fibula), causing pain on both the inside and outside of the ankle. As the foot spends increased time in a flattened, or deformed position, Arthritis can begin to affect the joints of the foot, causing additional pain.
Diagnosis
The history and physical examination are probably the most important tools the physician uses to diagnose this problem. The wear pattern on your shoes can offer some helpful clues. Muscle testing helps identify any areas of weakness or muscle impairment. This should be done in both the weight bearing and nonweight bearing positions. A very effective test is the single heel raise. You will be asked to stand on one foot and rise up on your toes. You should be able to lift your heel off the ground easily while keeping the calcaneus (heel bone) in the middle with slight inversion (turned inward). X-rays are often used to study the position, shape, and alignment of the bones in the feet and ankles. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating the posterior tibial tendon and spring ligament complex.
Non surgical Treatment
Although AAF is not reversible without surgery, appropriate treatment should address the patient?s current symptoms, attempt to reduce pain, and allow continued ambulation. In the early stages, orthotic and pedorthic solutions can address the loss of integrity of the foot?s support structures, potentially inhibiting further destruction.3-5 As a general principle, orthotic devices should only block or limit painful or destructive motion without reducing or restricting normal motion or muscle function. Consequently, the treatment must match the stage of the deformity.
Surgical Treatment
For patients with a more severe deformity, or significant symptoms that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary. There are several procedures available depending on the nature of your condition. Ligament and muscle lengthening, removal of inflamed tendon lining, transferring of a nearby tendon to re-establish an arch, and bone realignment and fusion are examples of surgical options to help with a painful flatfoot condition. Surgery can be avoided when symptoms are addressed early. If you are feeling ankle pain or notice any warmth, redness or swelling in your foot, contact us immediately. We can create a tailored treatment plan to resolve your symptoms and prevent future problems.
Pain In Left Foot Arch And Heel
Flat feet are a common condition. In infants and toddlers, the longitudinal arch is not developed and flat feet are normal. Most feet are flexible and an arch appears when the person stands on his or her toes. The arch develops in childhood, and by adulthood most people have developed normal arches. Most flat feet usually do not cause pain or other problems. Flat feet may be associated with pronation, a leaning inward of the ankle bones toward the center line. Shoes of children who pronate, when placed side by side, will lean toward each other (after they have been worn long enough for the foot position to remodel their shape). Foot pain, ankle pain or lower leg pain, especially in children, may be a result of flat feet and should be evaluated.

Causes
There are a number of possible causes for arch pain, but the most common are structural imbalances of the foot, such a pronated foot (rolls inward at the ankles). This is often not enough in isolation to cause the problem, but in combination with other factors arch pain may develop. These other factors are usually associated with overuse - running, walking, hard surfaces and/or OFAD (on feet all day), usually combined with inadequate or non-supportive footwear. The more common specific causes of arch pain can be plantar fasciitis (strain of the plantar fascia - a strong ligament that supports the arch), tarsal tunnel syndrome (a pinched nerve at the ankle that refers pain to the arch), foot strain from a pronated foot or flat foot, there can be osteoarthritis of the joints in the midfoot that can cause arch pain.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of plantar fasciitis include pain in the morning when you first get out of bed, pain and stiffness when you start to walk after sitting for a while, increasing arch or heel pain toward the end of the day, tired feet at the end of the day. Other causes of arch and heel pain include arthritis, infection, fractures and sprains, and even certain systemic diseases. Since there are multiple possible causes, you should see your podiatrist for a thorough evaluation if you are experiencing arch or heel pain that does not respond quickly to early treatment.
Diagnosis
The doctor will examine your feet for foot flexibility and range of motion and feel for any tenderness or bony abnormalities. Depending on the results of this physical examination, foot X-rays may be recommended. X-rays are always performed in a young child with rigid flatfeet and in an adult with acquired flatfeet due to trauma.
Non Surgical Treatment
Stretch the fascia. Prop your toes up against a wall, keeping your arch and heel flat so the toes stretch. Hold for a count of 10. Repeat 10 times three or four times per day. Roll a frozen water bottle under the arch. Stretch first then roll out the arch for 10 minutes; you don?t want to stretch the tendon when it?s ice cold. Freeze a golf ball and massage the fascia. Roll the frozen golf ball under the foot, starting from the front and working your way back. Put good pressure on each spot-the medial, center and lateral positions-for 15 seconds before moving to the next area. Then, roll the ball back and forth over the entire foot. Foam roll all muscles on the body above the plantar. Even tight shoulders can cause the condition, as your arm swing can throw off proper hip alignment and footstrike. Bump your arch. Get a commercial insole with an arch bump to push on the plantar and keep it from flexing-it doesn?t matter if you?re an under or overpronator; the plantar needs to be supported and strengthened, Wear the support in all shoes, if possible.

Surgical Treatment
The procedure involves cutting and shifting the bone, and then performing a tendon transfer. First, the surgeon performs a calcaneal osteotomy, cutting the heel bone and shifting it into the correct position. Second, the surgeon transfers the tendon. Reroute the flexor digitorum to replace the troublesome posterior tibial tendon. Finally, the surgeon typically performs one or more fine-tuning procedures that address the patient?s specific foot deformity. Often, the surgeon will lengthen the Achilles tendon because it is common for the mispositioned foot to cause the Achilles to tighten. Occasionally, to increase the arch, the surgeon performs another osteotomy of one of the bones of the midfoot. Occasionally, to point the foot in a straightforward direction, the surgeon performs another osteotomy of the outside portion of the calcaneus.
Stretching Exercises
Point your toes. To ease foot pain and aching in your feet, lift one foot and roll it downward until the toes are pointed toward the ground. Then flex your foot. Repeat using the other foot. This exercise will help stretch out all the small muscles that are on the bottom of your feet, which can help relieve aching and improve blood circulation. Raise your heels. This exercise is good for relieving toe cramps caused by standing for hours in constricting shoes, says Kurtz. Bonus: It can also strengthen calf muscles and make them look more defined. Stand up and lift your heels so that you are standing on the balls of your feet. Hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Squeeze your toes. To strengthen the toes and help alleviate foot pain from hammertoes (when a toe resembles a claw), separate your toes using corks or foam toe separators and then squeeze your toes together for five seconds. Repeat 10 times. Roll a ball. Want to create an instant massage for the bottom of your feet? Roll a golf ball or tennis ball under the ball of your foot. Apply light pressure for about two minutes. This exercise can be helpful for arch pain, cramps, and heel pain from plantar fasciitis. Stretch standing up. A weight-bearing, runners-type stretch can be helpful for foot pain in the arch. Stand up and place your toes against a wall; lean forward a little until you feel your arch stretch. Repeat using the other foot. Stretch sitting down. Sit barefoot and cross your left leg so that your ankle rests on your right thigh. Then hold your toes and bend them back toward your shin, stretching the band of tissue connecting the bottom of the heel to the ball. A University of Rochester study found that people living with plantar fasciitis had a 75 percent chance of having no pain within three to six months of performing this stretch three times daily. Give yourself a foot massage. Nothing spells pain relief like a good foot rub. Use the following technique recommended by Rhonda Crockett, a licensed massage therapist at Ohio State University?s Center for Integrative Medicine in Columbus. Start with your toes, using your thumb to massage them in circular motions. Then move to the arch under your foot and gradually work your way down to the heel, applying pressure with your fingers and palm of your hand. Use lotion to allow your hand to move smoothly over your foot. Relax in a warm bath with Epsom salts. The combination of warm water and Epsom salts will give you a double dose of pain relief and relaxation. Magnesium sulfate, the key compound in Epsom salts, has been found to relax muscles, reduce pain, and sedate the nervous system. Plus, warm water helps improve circulation in the feet and relieve muscle pain. Crockett recommends adding two cups of Epsom salts to a warm bath and soaking for 20 minutes.